TensorFlow.orgで表示 TensorFlow.orgで表示 |  GoogleColabで実行 GoogleColabで実行 |  GitHubでソースを表示 GitHubでソースを表示 |  ノートブックをダウンロード ノートブックをダウンロード |
概要
既定の推定量は、一般的なユースケースのTFLモデルをトレーニングするための迅速で簡単な方法です。このガイドでは、TFLの定型推定量を作成するために必要な手順の概要を説明します。
設定
TF Latticeパッケージのインストール:
pip install tensorflow-lattice
必要なパッケージのインポート:
import tensorflow as tf
import copy
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
import tensorflow_lattice as tfl
from tensorflow import feature_column as fc
logging.disable(sys.maxsize)
UCI Statlog(Heart)データセットのダウンロード:
csv_file = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'heart.csv', 'http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/heart.csv')
df = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
target = df.pop('target')
train_size = int(len(df) * 0.8)
train_x = df[:train_size]
train_y = target[:train_size]
test_x = df[train_size:]
test_y = target[train_size:]
df.head()
このガイドのトレーニングに使用されるデフォルト値の設定:
LEARNING_RATE = 0.01
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 500
PREFITTING_NUM_EPOCHS = 10
特徴列
他のTF推定用として、データはinput_fnを介して、典型的であり、使用して解析された推定器に渡される必要がFeatureColumnsを。
# Feature columns.
# - age
# - sex
# - cp chest pain type (4 values)
# - trestbps resting blood pressure
# - chol serum cholestoral in mg/dl
# - fbs fasting blood sugar > 120 mg/dl
# - restecg resting electrocardiographic results (values 0,1,2)
# - thalach maximum heart rate achieved
# - exang exercise induced angina
# - oldpeak ST depression induced by exercise relative to rest
# - slope the slope of the peak exercise ST segment
# - ca number of major vessels (0-3) colored by flourosopy
# - thal 3 = normal; 6 = fixed defect; 7 = reversable defect
feature_columns = [
fc.numeric_column('age', default_value=-1),
fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list('sex', [0, 1]),
fc.numeric_column('cp'),
fc.numeric_column('trestbps', default_value=-1),
fc.numeric_column('chol'),
fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list('fbs', [0, 1]),
fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list('restecg', [0, 1, 2]),
fc.numeric_column('thalach'),
fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list('exang', [0, 1]),
fc.numeric_column('oldpeak'),
fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list('slope', [0, 1, 2]),
fc.numeric_column('ca'),
fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list(
'thal', ['normal', 'fixed', 'reversible']),
]
TFLの定型推定器は、特徴列のタイプを使用して、使用するキャリブレーションレイヤーのタイプを決定します。私たちは、使用tfl.layers.PWLCalibration数値機能列の層とtfl.layers.CategoricalCalibrationカテゴリ機能列の層を。
カテゴリの特徴列は、埋め込み特徴列でラップされていないことに注意してください。それらは推定器に直接供給されます。
input_fnの作成
他の推定量と同様に、input_fnを使用して、トレーニングと評価のためにデータをモデルにフィードできます。 TFL推定器は、特徴の分位数を自動的に計算し、それらをPWLキャリブレーションレイヤーの入力キーポイントとして使用できます。そうするために、彼らは渡す必要feature_analysis_input_fn input_fnが、単一エポックまたはデータのサブサンプルと訓練に似ています、。
train_input_fn = tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.pandas_input_fn(
x=train_x,
y=train_y,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
num_epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
num_threads=1)
# feature_analysis_input_fn is used to collect statistics about the input.
feature_analysis_input_fn = tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.pandas_input_fn(
x=train_x,
y=train_y,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
# Note that we only need one pass over the data.
num_epochs=1,
num_threads=1)
test_input_fn = tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.pandas_input_fn(
x=test_x,
y=test_y,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
num_epochs=1,
num_threads=1)
# Serving input fn is used to create saved models.
serving_input_fn = (
tf.estimator.export.build_parsing_serving_input_receiver_fn(
feature_spec=fc.make_parse_example_spec(feature_columns)))
機能構成
機能のキャリブレーションごとの機能の構成が使用して設定されているtfl.configs.FeatureConfig 。機能の構成は、単調性の制約ごとの機能正則(参照が含まtfl.configs.RegularizerConfig )、および格子モデルのための格子サイズを。
何の設定が入力された特徴のために定義されていない場合、デフォルトで設定tfl.config.FeatureConfig使用されています。
# Feature configs are used to specify how each feature is calibrated and used.
feature_configs = [
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='age',
lattice_size=3,
# By default, input keypoints of pwl are quantiles of the feature.
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_clip_max=100,
# Per feature regularization.
regularizer_configs=[
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='calib_wrinkle', l2=0.1),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='cp',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=4,
# Keypoints can be uniformly spaced.
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints='uniform',
monotonicity='increasing',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='chol',
# Explicit input keypoint initialization.
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=[126.0, 210.0, 247.0, 286.0, 564.0],
monotonicity='increasing',
# Calibration can be forced to span the full output range by clamping.
pwl_calibration_clamp_min=True,
pwl_calibration_clamp_max=True,
# Per feature regularization.
regularizer_configs=[
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='calib_hessian', l2=1e-4),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='fbs',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1)
monotonicity=[(0, 1)],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='trestbps',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
monotonicity='decreasing',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='thalach',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
monotonicity='decreasing',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='restecg',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1), output(0) <= output(2)
monotonicity=[(0, 1), (0, 2)],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='exang',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1)
monotonicity=[(0, 1)],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='oldpeak',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
monotonicity='increasing',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='slope',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1), output(1) <= output(2)
monotonicity=[(0, 1), (1, 2)],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='ca',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=4,
monotonicity='increasing',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='thal',
# Partial monotonicity:
# output(normal) <= output(fixed)
# output(normal) <= output(reversible)
monotonicity=[('normal', 'fixed'), ('normal', 'reversible')],
),
]
キャリブレーションされた線形モデル
TFL缶詰推定器を構築するために、からモデル構成を構築tfl.configs 。校正線形モデルを使用して構築されtfl.configs.CalibratedLinearConfig 。入力フィーチャに区分的線形およびカテゴリカルキャリブレーションを適用し、続いて線形結合とオプションの出力区分的線形キャリブレーションを適用します。出力キャリブレーションを使用する場合、または出力境界が指定されている場合、線形レイヤーはキャリブレーションされた入力に加重平均を適用します。
この例では、最初の5つのフィーチャにキャリブレーションされた線形モデルを作成します。私たちは、使用tfl.visualization校正プロットとモデルグラフをプロットします。
# Model config defines the model structure for the estimator.
model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLinearConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
use_bias=True,
output_calibration=True,
regularizer_configs=[
# Regularizer for the output calibrator.
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='output_calib_hessian', l2=1e-4),
])
# A CannedClassifier is constructed from the given model config.
estimator = tfl.estimators.CannedClassifier(
feature_columns=feature_columns[:5],
model_config=model_config,
feature_analysis_input_fn=feature_analysis_input_fn,
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE),
config=tf.estimator.RunConfig(tf_random_seed=42))
estimator.train(input_fn=train_input_fn)
results = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=test_input_fn)
print('Calibrated linear test AUC: {}'.format(results['auc']))
saved_model_path = estimator.export_saved_model(estimator.model_dir,
serving_input_fn)
model_graph = tfl.estimators.get_model_graph(saved_model_path)
tfl.visualization.draw_model_graph(model_graph)
2021-09-30 20:54:06.660239: E tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_driver.cc:271] failed call to cuInit: CUDA_ERROR_NO_DEVICE: no CUDA-capable device is detected Calibrated linear test AUC: 0.834586501121521
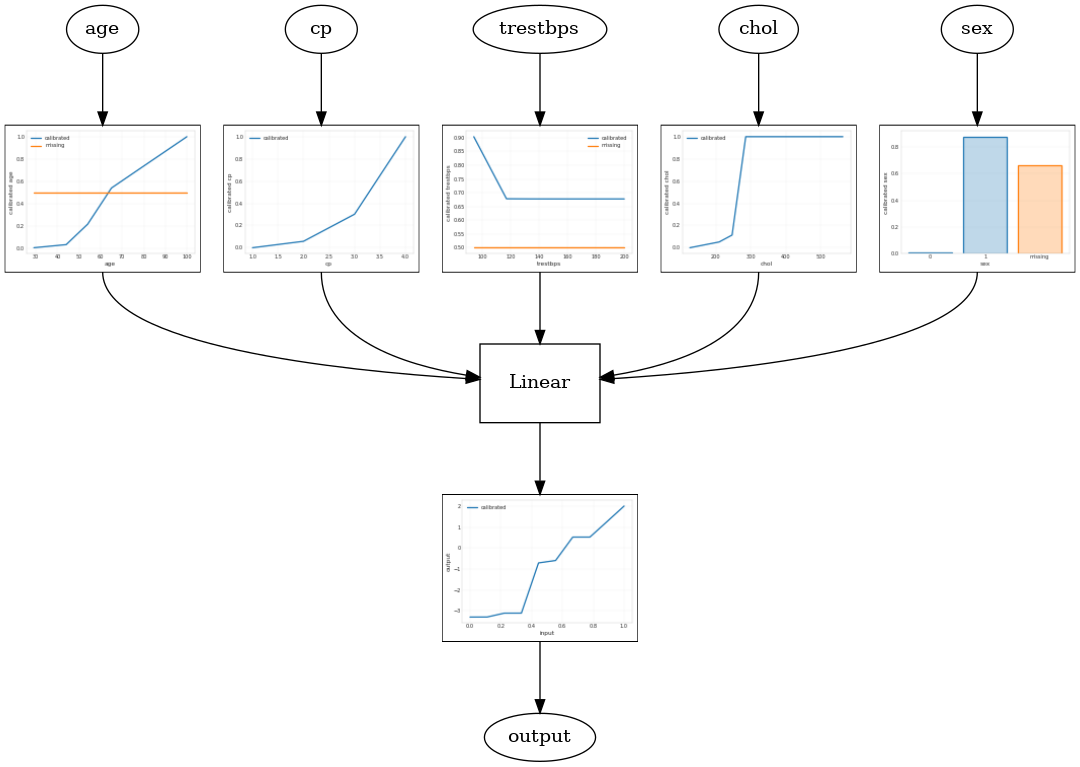
キャリブレーションされた格子モデル
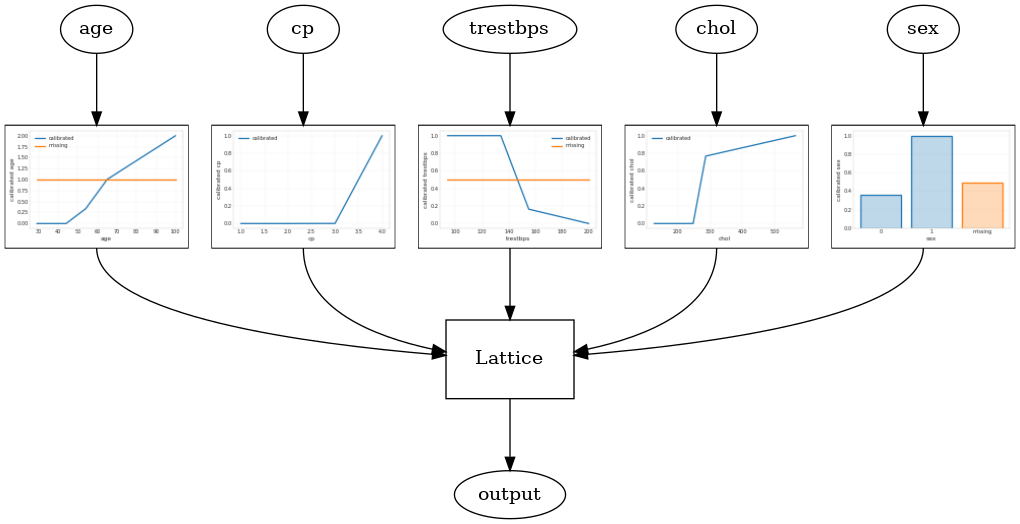
較正された格子モデルを使用して構築されtfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeConfig 。キャリブレーションされた格子モデルは、入力フィーチャに区分的線形およびカテゴリカルキャリブレーションを適用し、続いて格子モデルとオプションの出力区分的線形キャリブレーションを適用します。
この例では、最初の5つのフィーチャにキャリブレーションされたラティスモデルを作成します。
# This is calibrated lattice model: Inputs are calibrated, then combined
# non-linearly using a lattice layer.
model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
regularizer_configs=[
# Torsion regularizer applied to the lattice to make it more linear.
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='torsion', l2=1e-4),
# Globally defined calibration regularizer is applied to all features.
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='calib_hessian', l2=1e-4),
])
# A CannedClassifier is constructed from the given model config.
estimator = tfl.estimators.CannedClassifier(
feature_columns=feature_columns[:5],
model_config=model_config,
feature_analysis_input_fn=feature_analysis_input_fn,
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE),
config=tf.estimator.RunConfig(tf_random_seed=42))
estimator.train(input_fn=train_input_fn)
results = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=test_input_fn)
print('Calibrated lattice test AUC: {}'.format(results['auc']))
saved_model_path = estimator.export_saved_model(estimator.model_dir,
serving_input_fn)
model_graph = tfl.estimators.get_model_graph(saved_model_path)
tfl.visualization.draw_model_graph(model_graph)
Calibrated lattice test AUC: 0.8427318930625916
キャリブレーションされたラティスアンサンブル
フィーチャの数が多い場合は、アンサンブルモデルを使用できます。このモデルは、単一の巨大なラティスを作成する代わりに、フィーチャのサブセットに対して複数の小さなラティスを作成し、それらの出力を平均化します。アンサンブル格子モデルを使用して構築されているtfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig 。キャリブレーションされたラティスアンサンブルモデルは、入力フィーチャに区分的線形およびカテゴリカルキャリブレーションを適用し、続いてラティスモデルのアンサンブルとオプションの出力区分的リニアキャリブレーションを適用します。
ランダムラティスアンサンブル
次のモデル構成では、各ラティスの特徴のランダムなサブセットを使用します。
# This is random lattice ensemble model with separate calibration:
# model output is the average output of separately calibrated lattices.
model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
num_lattices=5,
lattice_rank=3)
# A CannedClassifier is constructed from the given model config.
estimator = tfl.estimators.CannedClassifier(
feature_columns=feature_columns,
model_config=model_config,
feature_analysis_input_fn=feature_analysis_input_fn,
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE),
config=tf.estimator.RunConfig(tf_random_seed=42))
estimator.train(input_fn=train_input_fn)
results = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=test_input_fn)
print('Random ensemble test AUC: {}'.format(results['auc']))
saved_model_path = estimator.export_saved_model(estimator.model_dir,
serving_input_fn)
model_graph = tfl.estimators.get_model_graph(saved_model_path)
tfl.visualization.draw_model_graph(model_graph, calibrator_dpi=15)
Random ensemble test AUC: 0.9003759026527405
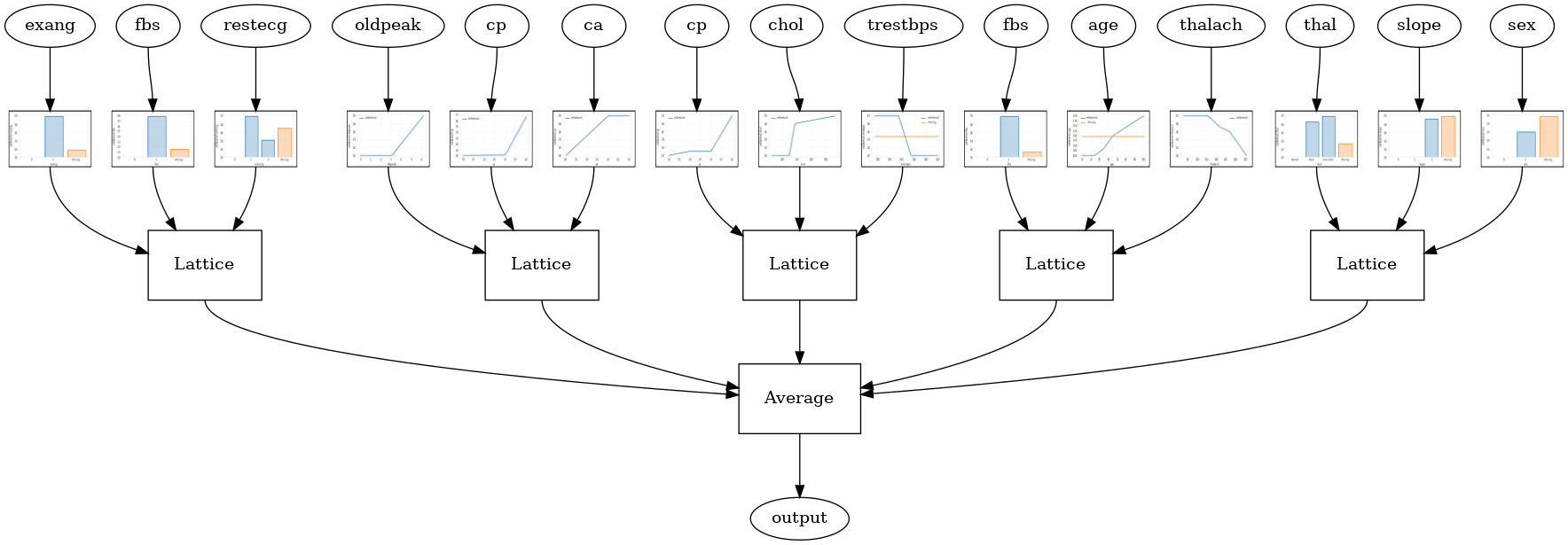
RTLレイヤーランダムラティスアンサンブル
以下のモデルの設定は、使用tfl.layers.RTL各格子のための機能のランダムなサブセットを使用する層。私たちは、ご注意tfl.layers.RTL唯一の単調性制約をサポートし、すべての機能を同じ格子サイズとノーごとの機能正則を持っている必要があります。使用していることを注意tfl.layers.RTL層はあなたが別の使用するよりもはるかに大きいアンサンブルまで拡張することができますtfl.layers.Latticeインスタンスを。
# Make sure our feature configs have the same lattice size, no per-feature
# regularization, and only monotonicity constraints.
rtl_layer_feature_configs = copy.deepcopy(feature_configs)
for feature_config in rtl_layer_feature_configs:
feature_config.lattice_size = 2
feature_config.unimodality = 'none'
feature_config.reflects_trust_in = None
feature_config.dominates = None
feature_config.regularizer_configs = None
# This is RTL layer ensemble model with separate calibration:
# model output is the average output of separately calibrated lattices.
model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig(
lattices='rtl_layer',
feature_configs=rtl_layer_feature_configs,
num_lattices=5,
lattice_rank=3)
# A CannedClassifier is constructed from the given model config.
estimator = tfl.estimators.CannedClassifier(
feature_columns=feature_columns,
model_config=model_config,
feature_analysis_input_fn=feature_analysis_input_fn,
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE),
config=tf.estimator.RunConfig(tf_random_seed=42))
estimator.train(input_fn=train_input_fn)
results = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=test_input_fn)
print('Random ensemble test AUC: {}'.format(results['auc']))
saved_model_path = estimator.export_saved_model(estimator.model_dir,
serving_input_fn)
model_graph = tfl.estimators.get_model_graph(saved_model_path)
tfl.visualization.draw_model_graph(model_graph, calibrator_dpi=15)
Random ensemble test AUC: 0.8903509378433228
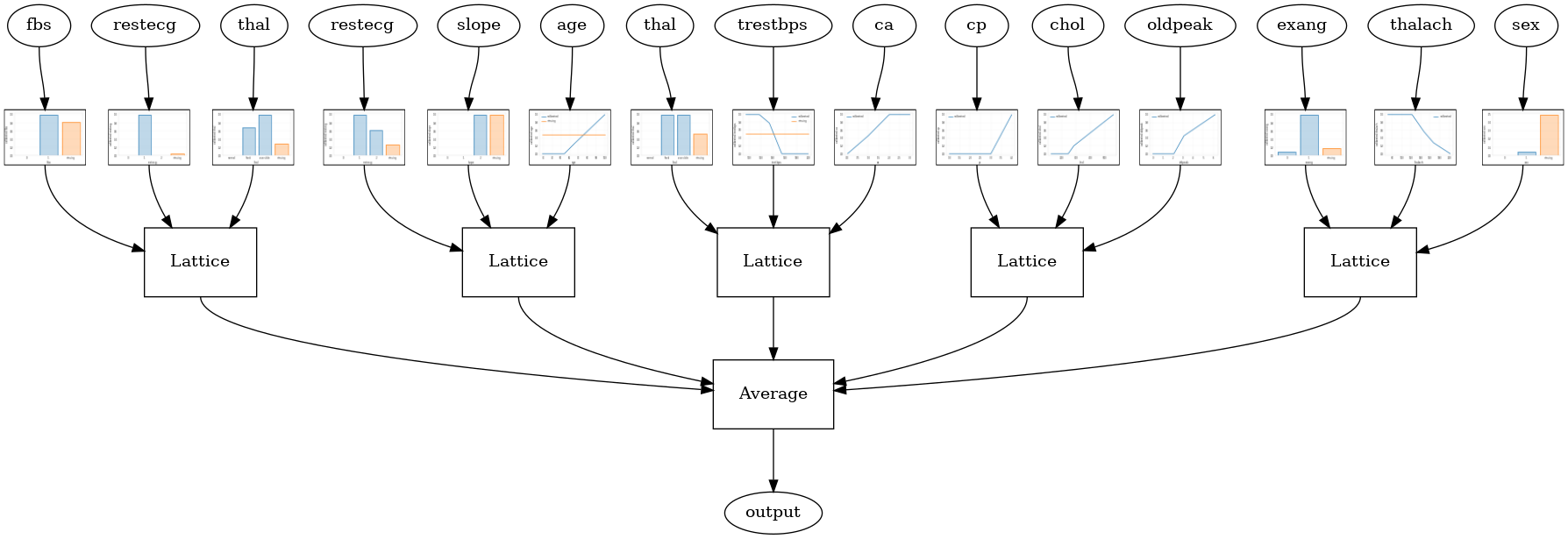
クリスタルラティスアンサンブル
TFLも呼ばれるヒューリスティック機能配置アルゴリズム、提供クリスタル。結晶は、最初の列車にペアごとの機能の相互作用を推定prefittingモデルをアルゴリズムです。次に、より非線形な相互作用を持つフィーチャが同じ格子内にあるように、最終的なアンサンブルを配置します。
結晶モデルの場合、あなたはまた、提供する必要がありますprefitting_input_fn前述したように、prefittingモデルを訓練するために使用されます。事前調整モデルは完全にトレーニングする必要がないため、いくつかのエポックで十分です。
prefitting_input_fn = tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.pandas_input_fn(
x=train_x,
y=train_y,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
num_epochs=PREFITTING_NUM_EPOCHS,
num_threads=1)
次に、設定することで、クリスタルモデルを作成することができlattice='crystals'モデルの設定で。
# This is Crystals ensemble model with separate calibration: model output is
# the average output of separately calibrated lattices.
model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
lattices='crystals',
num_lattices=5,
lattice_rank=3)
# A CannedClassifier is constructed from the given model config.
estimator = tfl.estimators.CannedClassifier(
feature_columns=feature_columns,
model_config=model_config,
feature_analysis_input_fn=feature_analysis_input_fn,
# prefitting_input_fn is required to train the prefitting model.
prefitting_input_fn=prefitting_input_fn,
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE),
prefitting_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE),
config=tf.estimator.RunConfig(tf_random_seed=42))
estimator.train(input_fn=train_input_fn)
results = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=test_input_fn)
print('Crystals ensemble test AUC: {}'.format(results['auc']))
saved_model_path = estimator.export_saved_model(estimator.model_dir,
serving_input_fn)
model_graph = tfl.estimators.get_model_graph(saved_model_path)
tfl.visualization.draw_model_graph(model_graph, calibrator_dpi=15)
Crystals ensemble test AUC: 0.8840851783752441
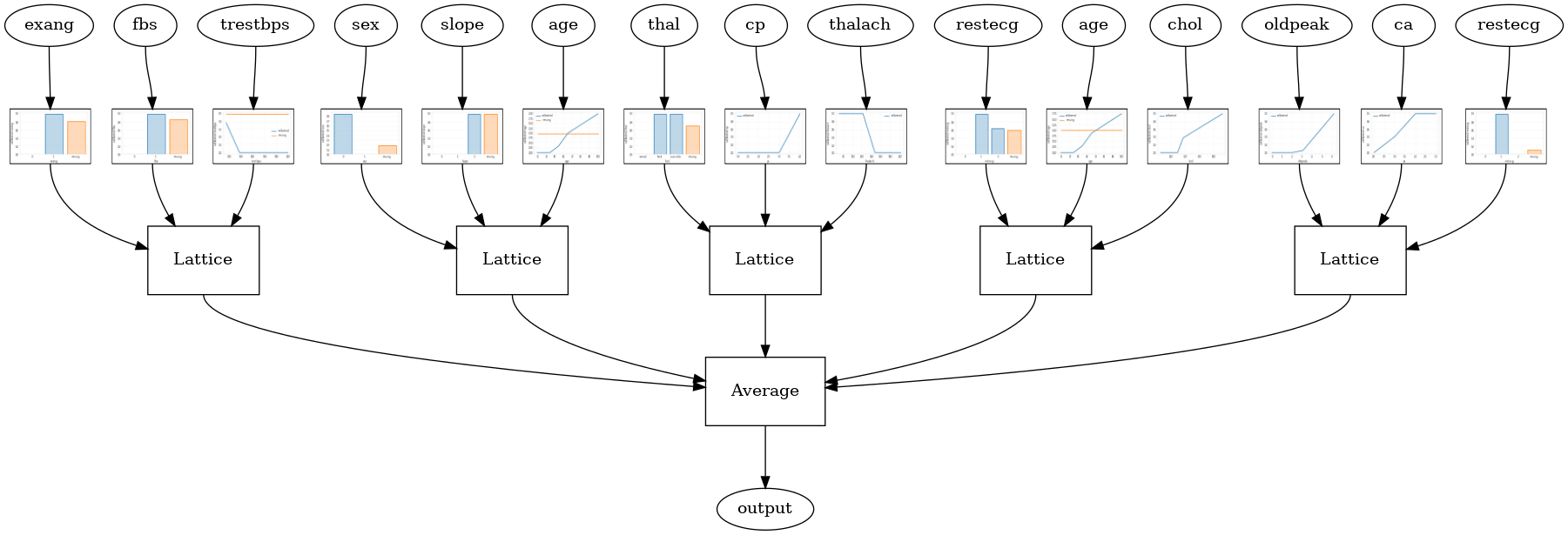
あなたは使用して、より詳細に機能キャリブレータをプロットすることができtfl.visualizationモジュールを。
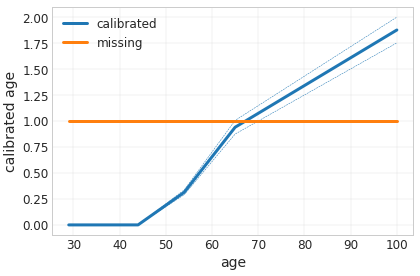
_ = tfl.visualization.plot_feature_calibrator(model_graph, "age")
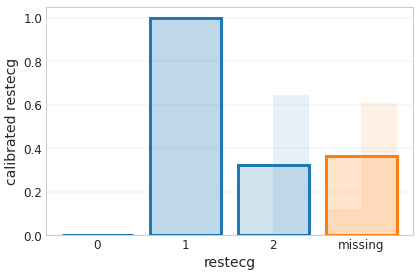
_ = tfl.visualization.plot_feature_calibrator(model_graph, "restecg")