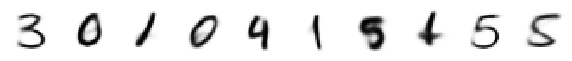在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 |
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行 |
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 |
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本 |
在本示例中,我们将展示如何使用 TFP 的“概率层”来拟合变分自动编码器。
依赖项和前提条件
Import
import numpy as np
import tensorflow.compat.v2 as tf
tf.enable_v2_behavior()
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
tfk = tf.keras
tfkl = tf.keras.layers
tfpl = tfp.layers
tfd = tfp.distributions
加快速度!
在深入探究之前,请确保我们在此演示中使用 GPU。
为此,请选择“Runtime” -> “Change runtime type” -> “Hardware accelerator” -> “GPU”。
以下代码段将验证我们是否有权访问 GPU。
if tf.test.gpu_device_name() != '/device:GPU:0':
print('WARNING: GPU device not found.')
else:
print('SUCCESS: Found GPU: {}'.format(tf.test.gpu_device_name()))
SUCCESS: Found GPU: /device:GPU:0
注:如果由于某种原因无法访问 GPU,此 Colab 将仍然有效。(但训练将花费更长时间。)
加载数据集
datasets, datasets_info = tfds.load(name='mnist',
with_info=True,
as_supervised=False)
def _preprocess(sample):
image = tf.cast(sample['image'], tf.float32) / 255. # Scale to unit interval.
image = image < tf.random.uniform(tf.shape(image)) # Randomly binarize.
return image, image
train_dataset = (datasets['train']
.map(_preprocess)
.batch(256)
.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
.shuffle(int(10e3)))
eval_dataset = (datasets['test']
.map(_preprocess)
.batch(256)
.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE))
请注意,上面的 preprocess() 会返回 image, image 而不是仅返回 image,因为 Keras 是为具有(样本,标签)输入格式(即,\(p\theta(y|x)\))的判别模型设置的。由于 VAE 的目标是从 x 本身(即,\(p_\theta(x|x)\))恢复输入 x,因此数据对为(样本,样本)。
VAE 代码高尔夫
指定模型。
input_shape = datasets_info.features['image'].shape
encoded_size = 16
base_depth = 32
prior = tfd.Independent(tfd.Normal(loc=tf.zeros(encoded_size), scale=1),
reinterpreted_batch_ndims=1)
encoder = tfk.Sequential([
tfkl.InputLayer(input_shape=input_shape),
tfkl.Lambda(lambda x: tf.cast(x, tf.float32) - 0.5),
tfkl.Conv2D(base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(4 * encoded_size, 7, strides=1,
padding='valid', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Flatten(),
tfkl.Dense(tfpl.MultivariateNormalTriL.params_size(encoded_size),
activation=None),
tfpl.MultivariateNormalTriL(
encoded_size,
activity_regularizer=tfpl.KLDivergenceRegularizer(prior)),
])
WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/linalg/linear_operator_lower_triangular.py:158: calling LinearOperator.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.ops.linalg.linear_operator) with graph_parents is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Do not pass `graph_parents`. They will no longer be used. WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/linalg/linear_operator_lower_triangular.py:158: calling LinearOperator.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.ops.linalg.linear_operator) with graph_parents is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Do not pass `graph_parents`. They will no longer be used.
decoder = tfk.Sequential([
tfkl.InputLayer(input_shape=[encoded_size]),
tfkl.Reshape([1, 1, encoded_size]),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(2 * base_depth, 7, strides=1,
padding='valid', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(filters=1, kernel_size=5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=None),
tfkl.Flatten(),
tfpl.IndependentBernoulli(input_shape, tfd.Bernoulli.logits),
])
vae = tfk.Model(inputs=encoder.inputs,
outputs=decoder(encoder.outputs[0]))
进行推断。
negloglik = lambda x, rv_x: -rv_x.log_prob(x)
vae.compile(optimizer=tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-3),
loss=negloglik)
_ = vae.fit(train_dataset,
epochs=15,
validation_data=eval_dataset)
Epoch 1/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 61ms/step - loss: 206.5541 - val_loss: 163.1924 Epoch 2/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 59ms/step - loss: 151.1891 - val_loss: 143.6748 Epoch 3/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 141.3275 - val_loss: 137.9188 Epoch 4/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 136.7453 - val_loss: 133.2726 Epoch 5/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 132.3803 - val_loss: 131.8343 Epoch 6/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 129.2451 - val_loss: 127.1935 Epoch 7/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 59ms/step - loss: 126.0975 - val_loss: 123.6789 Epoch 8/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 124.0565 - val_loss: 122.5058 Epoch 9/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 122.9974 - val_loss: 121.9544 Epoch 10/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 121.7349 - val_loss: 120.8735 Epoch 11/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 121.0856 - val_loss: 120.1340 Epoch 12/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 120.2232 - val_loss: 121.3554 Epoch 13/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 119.8123 - val_loss: 119.2351 Epoch 14/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 119.2685 - val_loss: 118.2133 Epoch 15/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 59ms/step - loss: 118.8895 - val_loss: 119.4771
妈妈快看,不用手张量!
# We'll just examine ten random digits.
x = next(iter(eval_dataset))[0][:10]
xhat = vae(x)
assert isinstance(xhat, tfd.Distribution)
Image Plot Util
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def display_imgs(x, y=None):
if not isinstance(x, (np.ndarray, np.generic)):
x = np.array(x)
plt.ioff()
n = x.shape[0]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, n, figsize=(n, 1))
if y is not None:
fig.suptitle(np.argmax(y, axis=1))
for i in range(n):
axs.flat[i].imshow(x[i].squeeze(), interpolation='none', cmap='gray')
axs.flat[i].axis('off')
plt.show()
plt.close()
plt.ion()
print('Originals:')
display_imgs(x)
print('Decoded Random Samples:')
display_imgs(xhat.sample())
print('Decoded Modes:')
display_imgs(xhat.mode())
print('Decoded Means:')
display_imgs(xhat.mean())
Originals:
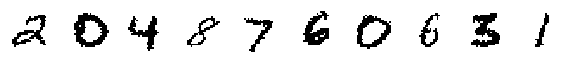
Decoded Modes:

Decoded Modes:
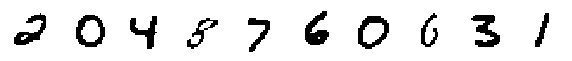
Decoded Means:
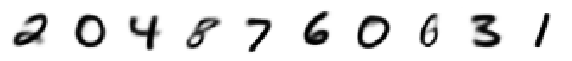
# Now, let's generate ten never-before-seen digits.
z = prior.sample(10)
xtilde = decoder(z)
assert isinstance(xtilde, tfd.Distribution)
print('Randomly Generated Samples:')
display_imgs(xtilde.sample())
print('Randomly Generated Modes:')
display_imgs(xtilde.mode())
print('Randomly Generated Means:')
display_imgs(xtilde.mean())
Randomly Generated Samples:
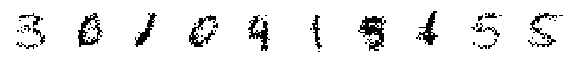
Randomly Generated Means:
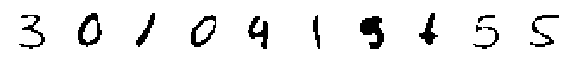
Randomly Generated Means: