 Voir sur TensorFlow.org Voir sur TensorFlow.org |  Exécuter dans Google Colab Exécuter dans Google Colab |  Voir sur GitHub Voir sur GitHub |  Télécharger le cahier Télécharger le cahier |  Voir les modèles TF Hub Voir les modèles TF Hub |
introduction
Les modèles de classification d'images ont des millions de paramètres. Les former à partir de zéro nécessite beaucoup de données de formation étiquetées et beaucoup de puissance de calcul. L'apprentissage par transfert est une technique qui raccourcit une grande partie de cela en prenant un morceau d'un modèle qui a déjà été formé sur une tâche connexe et en le réutilisant dans un nouveau modèle.
Ce Colab montre comment créer un modèle Keras pour classer cinq espèces de fleurs à l'aide d'un modèle pré-entraîné TF2 SavedModel de TensorFlow Hub pour l'extraction de caractéristiques d'image, entraîné sur l'ensemble de données ImageNet beaucoup plus grand et plus général. En option, l'extracteur de caractéristiques peut être entraîné ("affiné") avec le classificateur nouvellement ajouté.
Vous cherchez plutôt un outil ?
Il s'agit d'un didacticiel de codage TensorFlow. Si vous voulez un outil qui construit juste le modèle tensorflow ou TFLite pour, jetez un oeil à l' make_image_classifier outil de ligne de commande qui obtient installé par le package PIP tensorflow-hub[make_image_classifier] , ou à ce colab TFLite.
Installer
import itertools
import os
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
print("TF version:", tf.__version__)
print("Hub version:", hub.__version__)
print("GPU is", "available" if tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU') else "NOT AVAILABLE")
TF version: 2.7.0 Hub version: 0.12.0 GPU is available
Sélectionnez le module TF2 SavedModel à utiliser
Pour commencer, utilisez https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_100_224/feature_vector/4 . La même URL peut être utilisée dans le code pour identifier le SavedModel et dans votre navigateur pour afficher sa documentation. (Notez que les modèles au format TF1 Hub ne fonctionneront pas ici.)
Vous pouvez trouver plus de modèles de TF2 qui génèrent des vecteurs de caractéristiques d'image ici .
Il existe plusieurs modèles possibles à essayer. Tout ce que vous avez à faire est d'en sélectionner un autre dans la cellule ci-dessous et de poursuivre avec le bloc-notes.
model_name = "efficientnetv2-xl-21k" # @param ['efficientnetv2-s', 'efficientnetv2-m', 'efficientnetv2-l', 'efficientnetv2-s-21k', 'efficientnetv2-m-21k', 'efficientnetv2-l-21k', 'efficientnetv2-xl-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b0-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b1-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b2-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b3-21k', 'efficientnetv2-s-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-m-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-l-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-xl-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b0-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b1-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b2-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b3-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b0', 'efficientnetv2-b1', 'efficientnetv2-b2', 'efficientnetv2-b3', 'efficientnet_b0', 'efficientnet_b1', 'efficientnet_b2', 'efficientnet_b3', 'efficientnet_b4', 'efficientnet_b5', 'efficientnet_b6', 'efficientnet_b7', 'bit_s-r50x1', 'inception_v3', 'inception_resnet_v2', 'resnet_v1_50', 'resnet_v1_101', 'resnet_v1_152', 'resnet_v2_50', 'resnet_v2_101', 'resnet_v2_152', 'nasnet_large', 'nasnet_mobile', 'pnasnet_large', 'mobilenet_v2_100_224', 'mobilenet_v2_130_224', 'mobilenet_v2_140_224', 'mobilenet_v3_small_100_224', 'mobilenet_v3_small_075_224', 'mobilenet_v3_large_100_224', 'mobilenet_v3_large_075_224']
model_handle_map = {
"efficientnetv2-s": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_s/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-m": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_m/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-l": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_l/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-s-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_s/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-m-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_m/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-l-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_l/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_xl/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b0/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b1/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b2/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b3/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-s-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_s/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-m-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_m/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-l-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_l/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_xl/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b0/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b1/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b2/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b3/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b0": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b0/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b1": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b1/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b2": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b2/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b3": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b3/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnet_b0": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b0/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b1": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b1/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b2": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b2/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b3": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b3/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b4": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b4/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b5": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b5/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b6": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b6/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b7": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b7/feature-vector/1",
"bit_s-r50x1": "https://tfhub.dev/google/bit/s-r50x1/1",
"inception_v3": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/inception_v3/feature-vector/4",
"inception_resnet_v2": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/inception_resnet_v2/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v1_50": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v1_50/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v1_101": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v1_101/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v1_152": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v1_152/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v2_50": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v2_50/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v2_101": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v2_101/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v2_152": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v2_152/feature-vector/4",
"nasnet_large": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/nasnet_large/feature_vector/4",
"nasnet_mobile": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/nasnet_mobile/feature_vector/4",
"pnasnet_large": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/pnasnet_large/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v2_100_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_100_224/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v2_130_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_130_224/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v2_140_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_140_224/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v3_small_100_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_small_100_224/feature_vector/5",
"mobilenet_v3_small_075_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_small_075_224/feature_vector/5",
"mobilenet_v3_large_100_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_large_100_224/feature_vector/5",
"mobilenet_v3_large_075_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_large_075_224/feature_vector/5",
}
model_image_size_map = {
"efficientnetv2-s": 384,
"efficientnetv2-m": 480,
"efficientnetv2-l": 480,
"efficientnetv2-b0": 224,
"efficientnetv2-b1": 240,
"efficientnetv2-b2": 260,
"efficientnetv2-b3": 300,
"efficientnetv2-s-21k": 384,
"efficientnetv2-m-21k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-l-21k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k": 512,
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k": 224,
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k": 240,
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k": 260,
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k": 300,
"efficientnetv2-s-21k-ft1k": 384,
"efficientnetv2-m-21k-ft1k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-l-21k-ft1k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k-ft1k": 512,
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k-ft1k": 224,
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k-ft1k": 240,
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k-ft1k": 260,
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k-ft1k": 300,
"efficientnet_b0": 224,
"efficientnet_b1": 240,
"efficientnet_b2": 260,
"efficientnet_b3": 300,
"efficientnet_b4": 380,
"efficientnet_b5": 456,
"efficientnet_b6": 528,
"efficientnet_b7": 600,
"inception_v3": 299,
"inception_resnet_v2": 299,
"nasnet_large": 331,
"pnasnet_large": 331,
}
model_handle = model_handle_map.get(model_name)
pixels = model_image_size_map.get(model_name, 224)
print(f"Selected model: {model_name} : {model_handle}")
IMAGE_SIZE = (pixels, pixels)
print(f"Input size {IMAGE_SIZE}")
BATCH_SIZE = 16
Selected model: efficientnetv2-xl-21k : https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_xl/feature_vector/2 Input size (512, 512)
Configurer le jeu de données Flowers
Les entrées sont convenablement redimensionnées pour le module sélectionné. L'augmentation de l'ensemble de données (c'est-à-dire les distorsions aléatoires d'une image à chaque lecture) améliore l'apprentissage, en particulier. lors du réglage fin.
data_dir = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'flower_photos',
'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz',
untar=True)
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz 228818944/228813984 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step 228827136/228813984 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step
def build_dataset(subset):
return tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir,
validation_split=.20,
subset=subset,
label_mode="categorical",
# Seed needs to provided when using validation_split and shuffle = True.
# A fixed seed is used so that the validation set is stable across runs.
seed=123,
image_size=IMAGE_SIZE,
batch_size=1)
train_ds = build_dataset("training")
class_names = tuple(train_ds.class_names)
train_size = train_ds.cardinality().numpy()
train_ds = train_ds.unbatch().batch(BATCH_SIZE)
train_ds = train_ds.repeat()
normalization_layer = tf.keras.layers.Rescaling(1. / 255)
preprocessing_model = tf.keras.Sequential([normalization_layer])
do_data_augmentation = False
if do_data_augmentation:
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomRotation(40))
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomTranslation(0, 0.2))
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomTranslation(0.2, 0))
# Like the old tf.keras.preprocessing.image.ImageDataGenerator(),
# image sizes are fixed when reading, and then a random zoom is applied.
# If all training inputs are larger than image_size, one could also use
# RandomCrop with a batch size of 1 and rebatch later.
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomZoom(0.2, 0.2))
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomFlip(mode="horizontal"))
train_ds = train_ds.map(lambda images, labels:
(preprocessing_model(images), labels))
val_ds = build_dataset("validation")
valid_size = val_ds.cardinality().numpy()
val_ds = val_ds.unbatch().batch(BATCH_SIZE)
val_ds = val_ds.map(lambda images, labels:
(normalization_layer(images), labels))
Found 3670 files belonging to 5 classes. Using 2936 files for training. Found 3670 files belonging to 5 classes. Using 734 files for validation.
Définir le modèle
Il suffit de mettre un classificateur linéaire au - dessus du feature_extractor_layer avec le module Hub.
Pour la vitesse, nous commençons avec un non-trainable feature_extractor_layer , mais vous pouvez également activer peaufinage pour une plus grande précision.
do_fine_tuning = False
print("Building model with", model_handle)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
# Explicitly define the input shape so the model can be properly
# loaded by the TFLiteConverter
tf.keras.layers.InputLayer(input_shape=IMAGE_SIZE + (3,)),
hub.KerasLayer(model_handle, trainable=do_fine_tuning),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate=0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(len(class_names),
kernel_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(0.0001))
])
model.build((None,)+IMAGE_SIZE+(3,))
model.summary()
Building model with https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_xl/feature_vector/2
Model: "sequential_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
keras_layer (KerasLayer) (None, 1280) 207615832
dropout (Dropout) (None, 1280) 0
dense (Dense) (None, 5) 6405
=================================================================
Total params: 207,622,237
Trainable params: 6,405
Non-trainable params: 207,615,832
_________________________________________________________________
Entraîner le modèle
model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.005, momentum=0.9),
loss=tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True, label_smoothing=0.1),
metrics=['accuracy'])
steps_per_epoch = train_size // BATCH_SIZE
validation_steps = valid_size // BATCH_SIZE
hist = model.fit(
train_ds,
epochs=5, steps_per_epoch=steps_per_epoch,
validation_data=val_ds,
validation_steps=validation_steps).history
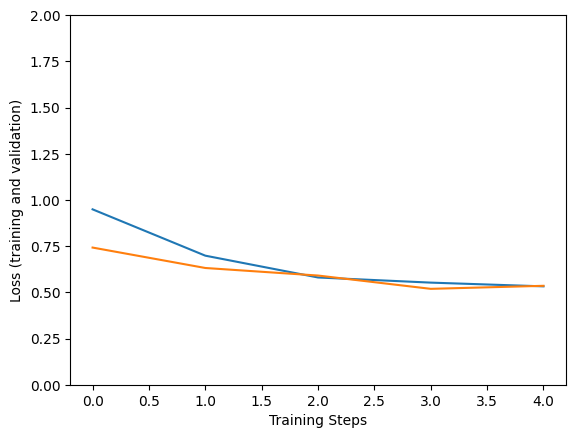
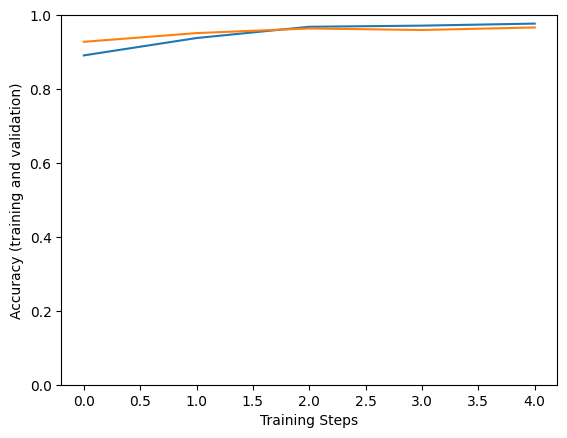
Epoch 1/5 183/183 [==============================] - 133s 543ms/step - loss: 0.9221 - accuracy: 0.8996 - val_loss: 0.6271 - val_accuracy: 0.9597 Epoch 2/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 514ms/step - loss: 0.6072 - accuracy: 0.9521 - val_loss: 0.5990 - val_accuracy: 0.9528 Epoch 3/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 513ms/step - loss: 0.5590 - accuracy: 0.9671 - val_loss: 0.5362 - val_accuracy: 0.9722 Epoch 4/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 514ms/step - loss: 0.5532 - accuracy: 0.9726 - val_loss: 0.5780 - val_accuracy: 0.9639 Epoch 5/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 513ms/step - loss: 0.5618 - accuracy: 0.9699 - val_loss: 0.5468 - val_accuracy: 0.9556
plt.figure()
plt.ylabel("Loss (training and validation)")
plt.xlabel("Training Steps")
plt.ylim([0,2])
plt.plot(hist["loss"])
plt.plot(hist["val_loss"])
plt.figure()
plt.ylabel("Accuracy (training and validation)")
plt.xlabel("Training Steps")
plt.ylim([0,1])
plt.plot(hist["accuracy"])
plt.plot(hist["val_accuracy"])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f607ad6ad90>]
Essayez le modèle sur une image à partir des données de validation :
x, y = next(iter(val_ds))
image = x[0, :, :, :]
true_index = np.argmax(y[0])
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# Expand the validation image to (1, 224, 224, 3) before predicting the label
prediction_scores = model.predict(np.expand_dims(image, axis=0))
predicted_index = np.argmax(prediction_scores)
print("True label: " + class_names[true_index])
print("Predicted label: " + class_names[predicted_index])

True label: sunflowers Predicted label: sunflowers
Enfin, le modèle formé peut être enregistré pour le déploiement sur TF Serving ou TFLite (sur mobile) comme suit.
saved_model_path = f"/tmp/saved_flowers_model_{model_name}"
tf.saved_model.save(model, saved_model_path)
2021-11-05 13:09:44.225508: W tensorflow/python/util/util.cc:368] Sets are not currently considered sequences, but this may change in the future, so consider avoiding using them. WARNING:absl:Found untraced functions such as restored_function_body, restored_function_body, restored_function_body, restored_function_body, restored_function_body while saving (showing 5 of 3985). These functions will not be directly callable after loading. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/saved_flowers_model_efficientnetv2-xl-21k/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/saved_flowers_model_efficientnetv2-xl-21k/assets
Facultatif : Déploiement sur TensorFlow Lite
Tensorflow Lite vous permet de déployer des modèles tensorflow aux appareils mobiles et IdO. Le code ci - dessous montre comment convertir le modèle formé pour TFLite et appliquer des outils de post-formation du modèle d' optimisation tensorflow Toolkit . Enfin, il l'exécute dans l'interpréteur TFLite pour examiner la qualité résultante
- La conversion sans optimisation fournit les mêmes résultats qu'auparavant (jusqu'à l'erreur d'arrondi).
- La conversion avec optimisation sans aucune donnée quantifie les poids du modèle à 8 bits, mais l'inférence utilise toujours le calcul à virgule flottante pour les activations du réseau de neurones. Cela réduit la taille du modèle presque d'un facteur 4 et améliore la latence du processeur sur les appareils mobiles.
- De plus, le calcul des activations du réseau neuronal peut également être quantifié en nombres entiers de 8 bits si un petit ensemble de données de référence est fourni pour calibrer la plage de quantification. Sur un appareil mobile, cela accélère encore l'inférence et permet de s'exécuter sur des accélérateurs comme Edge TPU.
Paramètres d'optimisation
optimize_lite_model = False
num_calibration_examples = 60
representative_dataset = None
if optimize_lite_model and num_calibration_examples:
# Use a bounded number of training examples without labels for calibration.
# TFLiteConverter expects a list of input tensors, each with batch size 1.
representative_dataset = lambda: itertools.islice(
([image[None, ...]] for batch, _ in train_ds for image in batch),
num_calibration_examples)
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(saved_model_path)
if optimize_lite_model:
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
if representative_dataset: # This is optional, see above.
converter.representative_dataset = representative_dataset
lite_model_content = converter.convert()
with open(f"/tmp/lite_flowers_model_{model_name}.tflite", "wb") as f:
f.write(lite_model_content)
print("Wrote %sTFLite model of %d bytes." %
("optimized " if optimize_lite_model else "", len(lite_model_content)))
2021-11-05 13:10:59.372672: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:363] Ignored output_format. 2021-11-05 13:10:59.372728: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:366] Ignored drop_control_dependency. 2021-11-05 13:10:59.372736: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:372] Ignored change_concat_input_ranges. WARNING:absl:Buffer deduplication procedure will be skipped when flatbuffer library is not properly loaded Wrote TFLite model of 826236388 bytes.
interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_content=lite_model_content)
# This little helper wraps the TFLite Interpreter as a numpy-to-numpy function.
def lite_model(images):
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
interpreter.set_tensor(interpreter.get_input_details()[0]['index'], images)
interpreter.invoke()
return interpreter.get_tensor(interpreter.get_output_details()[0]['index'])
num_eval_examples = 50
eval_dataset = ((image, label) # TFLite expects batch size 1.
for batch in train_ds
for (image, label) in zip(*batch))
count = 0
count_lite_tf_agree = 0
count_lite_correct = 0
for image, label in eval_dataset:
probs_lite = lite_model(image[None, ...])[0]
probs_tf = model(image[None, ...]).numpy()[0]
y_lite = np.argmax(probs_lite)
y_tf = np.argmax(probs_tf)
y_true = np.argmax(label)
count +=1
if y_lite == y_tf: count_lite_tf_agree += 1
if y_lite == y_true: count_lite_correct += 1
if count >= num_eval_examples: break
print("TFLite model agrees with original model on %d of %d examples (%g%%)." %
(count_lite_tf_agree, count, 100.0 * count_lite_tf_agree / count))
print("TFLite model is accurate on %d of %d examples (%g%%)." %
(count_lite_correct, count, 100.0 * count_lite_correct / count))
TFLite model agrees with original model on 50 of 50 examples (100%). TFLite model is accurate on 50 of 50 examples (100%).
